The most important things to know when a new member arrives at your family
A baby is born!! What do you do?
In the rapture of addition of the newest member of our family we celebratebut we also wish to ensure the baby gets the best of care.
Here is a list of things that must be taken into account from orthopaedic point of view.
- Consult your paediatrician and get the baby properly examined and weighed, ask for :
- Guidelines on feeding
- Immunisation schedule
- Care and training
- Review schedule
Most importantly discuss about future lookout points if there were trubles during child birth like:
- Baby cried late
- Baby was underweight or delivered before schedule time
- Baby had to be admitted to hospital post delivery
- Any disease of mother and child during pregnancy and post delivery period
- Consult your orthopaedician to ensure a complete evaluation of limb and spine.
- Keep an eye out for orthopaedic trouble signs:
- Some swelling over back or spine
- Baby keeping one or more of his/her limb in a peculiar posture
- Baby not moving one or more of her limbs or parts of limbs
- Count fingers and toes
- Most importantly always compare with the opposite side to be extra sure.
Remember most problems solve if u diagnose early Here is a list of common orthopaedic birth problems
Congenital club foot – A club foot looks like a club
How is it treated ?
You must get the baby examined by an orthopaedician as soon as possible. The universally accepted “Ponseti” correction method is started as soon as possible after birth and it consist of manipulation and weekly plaster cast application on the affected limb.
What can you expect?
The treatment universally adopted for club foot corrects most of the cases, However it is not a guarantee of cure. Your orthopaedician will discuss the prognosis of your baby only after proper evaluation and it may vary case to case.
Find what Dr. Sagnik Ray says about Club Foot
Spina Bifida
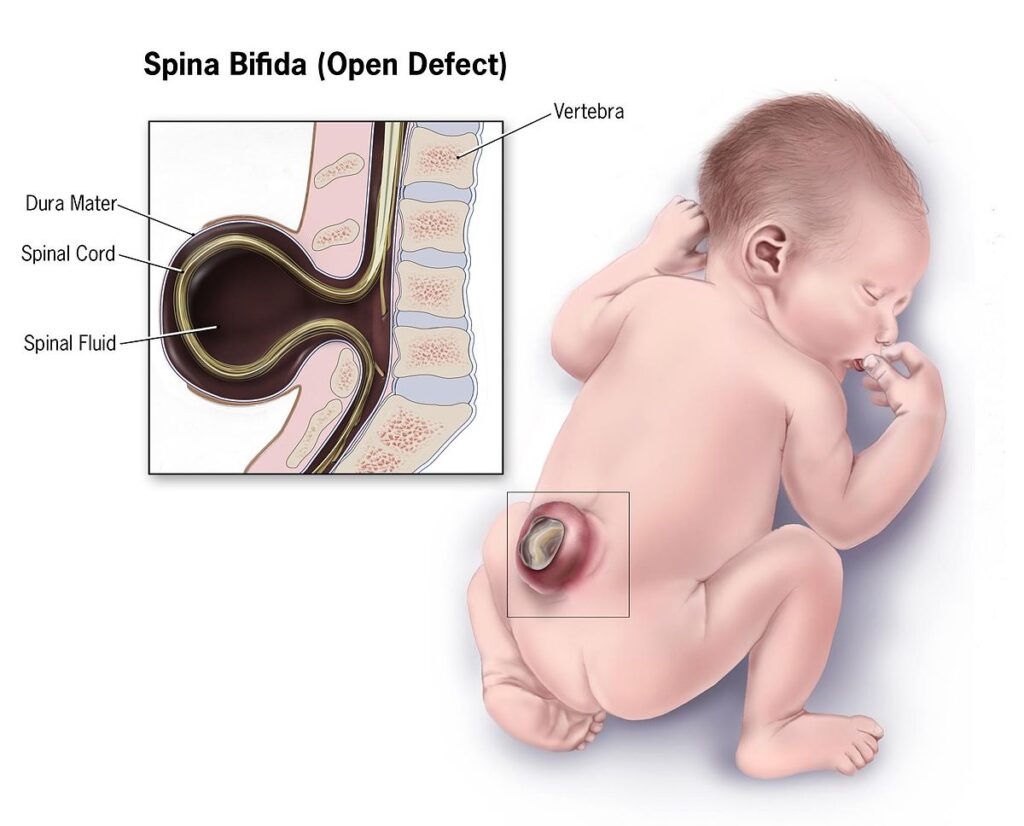
Spina bifida or spinal dysraphism is a condition in which one or more of the vertebra (bones guarding your spinal column in a protective arch) fail to fuse (form completely). This condition along with a host of other disorders can often be diagnosed or predicted even before the baby is born using modern diagnostic tools, for which you can consult your gynaecologist and paediatrician.
What do you see?
This is what do you see in cross section. If you are suspicious about this consult your paediatrician and neurosurgeon for management advice. As this condition often comes as a package deal with various other limb problems it is prudent to consult a competent orthopaedician for a thorough check-up.
Hip Dysplasia
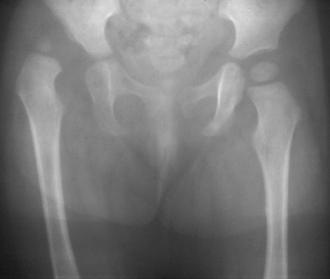
This is a congenital hipjoint anomaly that causes the child to keep the entire affected limb in a peculiar position, you may also hear a clicking sound from hip if you try to move the limb form that position.
What to do?
This condition is best managed within 6 months of age, and often become really difficult to cure in older age groups. You should consult your orthopaedician for consultation of proper management protocol of this problem as soon as u suspect it. From complete cure to disability remaining upto adulthood, this condition has a wide range of prognosis depending on the severity.
Wry Neck
Wry neck is a congenital condition often associated with minor birth injuries to neck
What to do?
This is another problem that should be managed early to avoid future disability that invariably amounts to disfigurement of face, eyesight problems and many more. Some cases are often cured with certain orthosis while others would need surgery, depending on severity and cause of the problem. Delay in consultation and planning in these cases is inviting catastrophe.
Infection
What is it?
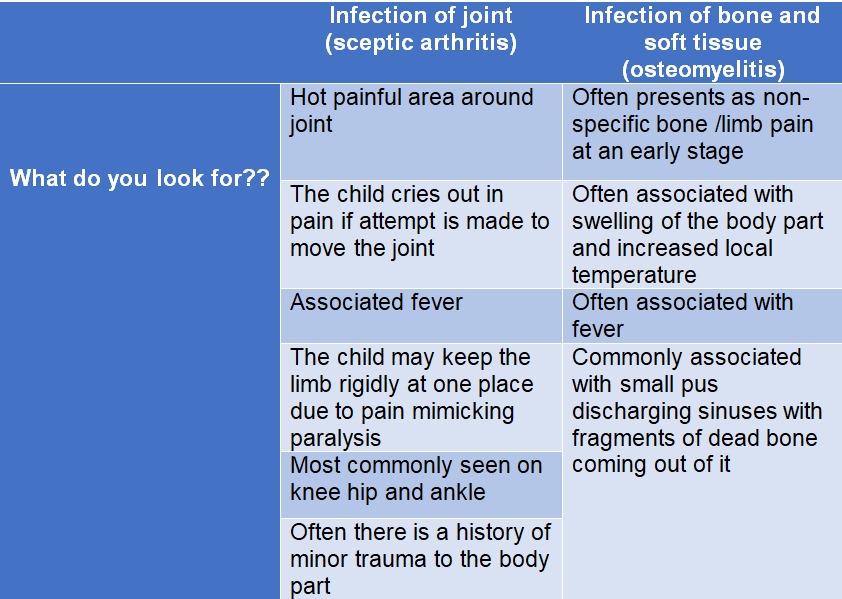
Orthopaedic infections can broadly divided into 2 common types:
What to do?
- A sceptic arthritis is a surgical emergency unless proven otherwise.
- An osteomyelitis also require as early as possible initiation of management to ensure better results.
- Unfortunately a chronic osteomyelitis is a long harrowing disease that often takes months even years to control.
- If you suspect any of these contact your orthopaedician as soon as possible.
Bone Swelling
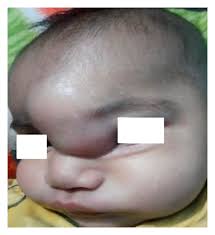
What is it?
A bone swelling can be of many types and severity and it’s not possible to draw up a comprehensive patient guide in a few lines, however some general points in this regard are helpful
- Bone swellings are commonly hard swellings that are inseparable from bones even if u push them
- All limb, spine and back swellings must be evaluated by an orthopaedician to ensure proper and timely management
- he urgent referral red flag signs are:
- Pain
- Redness and increased local temperature
- Fever
- Rapid increase in size over weeks or months
- Tingling, numbness, pain, reduced surface temperature over the distal part of the limb
Pulled Elbow
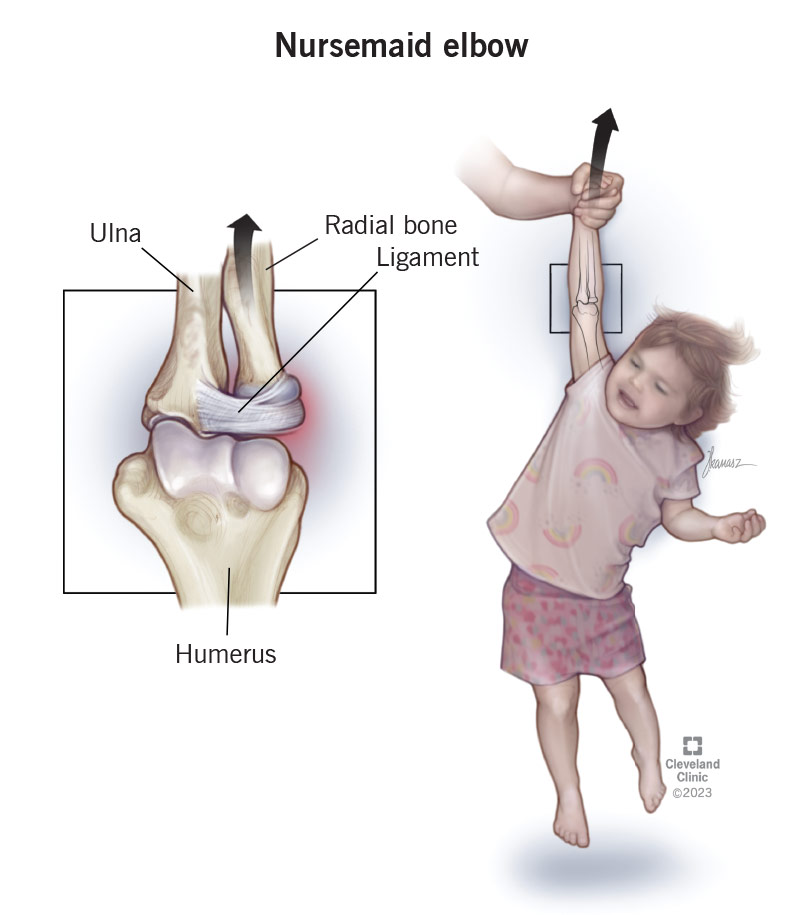
Inspired my TV or films caregivers often try to swing a child by holding his/her forearm
This is an absolute NO-NO for children of most age groups especially so in the early years as this action can precipitate many different kinds of injury to wrist, elbow or shoulder commonest of which is a pulled elbow
What do you see?
The injured child will hold the forearm and elbow in a peculiar position and cries on attempts to move it from position
What to do?
The child has to be taken to a paediatrician for immediate reduction
Prognosis?
This is usually a curable condition
Paediatric trauma
A paediatric trauma is different from adult trauma in 2 ways:
- The response time to treatment initiation must be faster to prevent catastrophic damage
- The child fares better than an adult with respect to healing in the long run once the emergency period is over.
There are 3 basic aspects of any limb trauma
- The bleeding wound
- The broken bone
- Nerve or blood vessel injury
So, if you come across a trauma victim you better arm yourself with the basic knowledge of how to respond to it to prevent lasting future damage
What to do about the wound?
- If the wound is small wash it with large amount of (upto 6 litres) drinking water to wash off all soil and dirt apply pressure on it with a piece of clean cloth or sterile gauze. Then wrap it with another clean piece of cloth or bandage firmly to stop bleeding

- If the wound is big with a lot of bleeding and undelying muscles and bones exposed just put pressure on it with a piece of clean cloth and wrap it with a bandage or another cloth and rush the patient to nearest hospital emergency

What to do about the fracture?
- A fractured limb needs to be splinted (supported) before rushing the patient to a hospital:
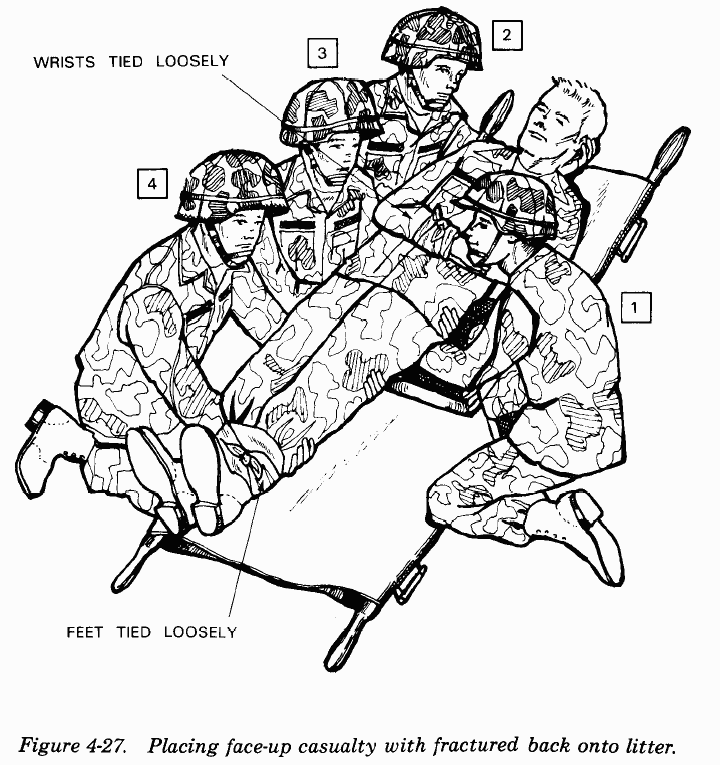
- for spine fractures the patient needs to be on a hard board with cervical support by pillow or cervical collar before any attempts are made to move him/her
- If you suspect injury to pelvis and help is not to be found nearby you can tie the pelvis and put the patient on a hardboard before u attempt to move him/her and then rush to the hospital

- Some materials easily accessible for splint making
- Few things to keep in mind while splinting
- Splint should be firm & ensure that there will be no movement of the injured limb
- The splint should supplemented with a sling or arm pouch bag for upper limb for comfort
- The splint should not be so tight that distal blood supply stopped
- Signs of loss of blood supply to a limb due to trauma
- Portion of the limb distal to injury site will be cold/cool to touch in comparison to opposite site
- The distal portion will look pale (whitish) compared to the opposite side
- If you know how to feel pulse you won’t be able to feel it distal to the injured site
- There may be extreme pain on the distal end of the limb.
- Signs of loss of nerve supply to distal to the site of injury.
- Patient cannot sense- touch on pinch distal to injured area
- There may be tingling or numbness distal to the injured area with pain
These are signs of extreme emergency and patient has to be rushed to a hospital or your nearest orthopaedician within 30 minutes of trauma.
Most paediatric trauma is more forgiving and faster healing than their adult counterpart (described in the trauma & emergency section) once the emergency period is over
